Window functions, a powerful feature in SQL, provide a way to perform calculations across a specified range of rows related to the current row. This article aims to demystify window functions, illustrating their usage through practical examples with a user table.
Understanding Window Functions
Window functions operate within a specific "window" or subset of rows defined by an OVER clause. These functions allow you to perform calculations on a set of rows related to the current row without the need for self-joins or subqueries.
Example User Table
For the purpose of this article, let's consider a user table named Users with columns: ID, Name, Email, and Age.
create database MyLearningDB use MyLearningDB create table Users ( id int primary key identity(1,1), fullname varchar(100), emailid varchar(200), age int ) insert into Users values ('user1','user1@email.com',33), ('user2','user2@email.com',53), ('user3','user3@email.com',63), ('user4','user4@email.com',70), ('user5','user5@email.com',40), ('user6','user6@email.com',22), ('user7','user7@email.com',46), ('user8','user8@email.com',88) select * from Users
Window Functions
Let's demonstrate some window functions with practical examples.
ROW_NUMBER()
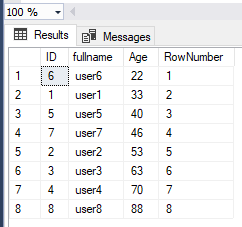
The ROW_NUMBER() function assigns a unique sequential integer to rows within the result set of a query.
SELECT ID, fullname, Age, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY Age) AS RowNumber FROM Users;
RANK()
The RANK() function assigns a rank to each row within the partition of a result set. If there are ties, the same rank is assigned to the tied rows, and the next rank is skipped.
SELECT ID, fullname, Age, RANK() OVER (ORDER BY Age) AS Rank FROM Users;
DENSE_RANK()
The DENSE_RANK() function is similar to RANK(), but it does not skip any ranks if there are ties.
SELECT ID, fullname, Age, DENSE_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY Age) AS DenseRank FROM Users;
Window functions are a powerful tool in SQL, allowing for sophisticated data analysis without the need for complex joins or subqueries. By understanding and utilizing these functions, you can perform a wide range of calculations and analyses more efficiently and effectively.
Explore and practice with these examples to deepen your understanding of window functions and enhance your SQL querying skills.
.png)